Light Bulb Buying Guide
-
-
How many people does it take to change a light bulb? Just one, once you understand how to pick the right one. In today’s market there are a variety of light bulbs available to you. You can control everything from how bright they look, the tone of the light, how much energy you can save and even what they can do!
-
-
 There are many lighting options for use in residential homes. Before purchasing a light bulb, consider where it will be used in your home. Areas such as kitchens, bathrooms and laundry rooms may have higher humidity levels than other rooms so it is recommended to search for UL Damp Listed light bulbs for those areas. If humidity isn’t a concern, simply choosing a product that has UL approval will give you extra piece of mind that your light bulb of choice is safe around your family.
There are many lighting options for use in residential homes. Before purchasing a light bulb, consider where it will be used in your home. Areas such as kitchens, bathrooms and laundry rooms may have higher humidity levels than other rooms so it is recommended to search for UL Damp Listed light bulbs for those areas. If humidity isn’t a concern, simply choosing a product that has UL approval will give you extra piece of mind that your light bulb of choice is safe around your family. -
 First, make sure you have an outdoor rated fixture. The fixture you choose to use outdoors will have certain specifications about the type of bulb you choose to use with it. You should also consider how much exposure to water the light bulb will have. UL is an organization which tests products for safety and if the light bulb has been tested to UL standards it should indicate if it can be used in areas exposed to water.
First, make sure you have an outdoor rated fixture. The fixture you choose to use outdoors will have certain specifications about the type of bulb you choose to use with it. You should also consider how much exposure to water the light bulb will have. UL is an organization which tests products for safety and if the light bulb has been tested to UL standards it should indicate if it can be used in areas exposed to water.
The first step toward buying the right light bulb is to determine the application. By doing this you will have a better idea of the specifications you’re looking for.
UL-Listed for Wet Locations
Outdoor locations exposed to wind, rain, snow, etc., including open-air decks, porches and gazebos.
UL-Listed for Damp Locations
Covered high-humidity outdoor spaces like patios or garages, where there’s no direct contact with rain or snow.
-
Ready to go the Extra Mile?
Pick a light bulb that is Energy Star qualified. Compact Fluorescent and LED light bulbs are eligible for Energy Star qualification. This rating means the light bulb meets energy efficiency levels that will greatly lower your energy consumption.
ENERGY STAR Certified Light Bulbs
- Use about 70-90% less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs
- Last 10 to 25 times longer and saves $30 to $80 in electricity costs over its lifetime
- Meet strict quality and efficiency standards that are tested by accredited labs and certified by a third party
- Produce about 70-90% less heat, so it’s safer to operate and can cut energy costs associated with home cooling
Only light bulbs with electrical components can be tested for UL Safety Standards and Energy Star performance standards. This means you will only see UL or ENERGY STAR references on CFL or LED products. Incandescent products including halogen and Krypton/Xenon bulbs do not have the opportunity to be rated by these organizations and are generally safe to use in any application as long as the light bulb’s wattage does not exceed the maximum wattage of the fixture.
-
Ambient, Task, Decorative or Accent Lighting LIGHTING FUNCTION AMBIENT TASK DECORATIVE ACCENT Description Overall illumination. Light for a specific task. Used to enhance design appeal. Used to highlight room features. Common Applications Large, Open Spaces such as: - Foyer
- Living Room
- Bedroom
- Basement
Small, work areas/spaces: - Kitchen
- Island / Counter
- Home Office Desk
- Near a Reading
- Chair
Decorative Fixtures Special objects or room features: - Statue
- Painting
- Pictures on a shelf
- Mantelpiece
Recommended Bulb Type Omni-Directional bulbs which emit light in all directions. - Chandelier
- Standard
- Globes
Directional Bulbs which emit light in a specific direction or omni-directional bulbs used in a fixture which directs light in a specific direction. - Reflector (MR16)
- In a Pendant
- Standard (A19)
- Portable Lamp
Omni-Directional bulbs which emit light in all directions. - Chandelier
- Standard
- Globes
- Nostalgic
Directional Bulbs which emit light in a specific direction. - Multi-Faceted
- Reflectors (MRs)
- Parabolic Aluminum
- Reflectors
- Reflectors (BRs & Rs)
-

Fixture Details
Your lighting fixture will determine many of the required specifications for your light bulb choice – here are a few of the specifications you’ll need to know before choosing your light bulb:
Bulb Type (Shape)
Decorative
Most fixtures will be either LOW VOLTAGE (12V) or LINE VOLTAGE (120V). The fixture you are using will indicate which voltage your bulb should be. Fixtures will also indicate the maximum wattage for bulbs. Any energy efficient technology such as halogen, CFL or LED will be much lower than the maximum wattage since most fixtures are basing this measurement off of old incandescent technology.
-
-
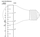
A Quick Guide to Bulb Size
All lamps have a specific “bulb type” designation that describes the shape of the lamp and the size of the lamp (diameter).
The reference ruler (pictured on the left) illustrates the most commonly used household lamp, an A19. The “A” indicates the shape (standard) and the diameter would be 2 3/8”, which is “19” eights of an inch. Additional popular lamp designations are also indicated on the reference ruler.
NOTE: NEWER TECHNOLOGIES DO NOT ALWAYS FOLLOW THESE GUIDELINES SO BE SURE TO CHECK THE BULBS MOL (Maximum Overall Length) and MOD (Maximum Overall Diameter) TO ENSURE THEY WILL FIT IN YOUR FIXTURE.
If the fixture is fully enclosed, you should check that the light bulb you are choosing can be used in fully enclosed fixtures. Some light bulbs such as CFLs and LEDs are not recommended for use in fully enclosed fixtures because heat may affect their electrical components.
If the fixture is not fully enclosed, you’ll need to determine the exposure it might have to water. UL is an organization which tests products for safety ratings and if the light bulb has been tested to UL standards it should indicate if it can be used in areas exposed to water.
-

Choose the Technology that Suits you
Due to the new energy efficient standards, many traditional incandescents are being phased out of the market. Now, you’ll see new energy efficient light bulbs available for purchase. Today, there are 3 popular choices of energy efficient light bulbs: halogen, compact fluorescent (CFL) or light emitting diode (LED).
Find the right option for you by first looking at the benefits of each energy efficient option: -
Dimmable Light Bulbs
Many people like to have the flexibility to dim their light bulbs. If you're one of them, read on.
Traditional incandescent or halogen light bulbs are fully dimmable. As they dim, they tend to glow warmer and create a nice ambiance. It's pretty simply because there are no electrical components inside of these bulbs. Newer technologies however are not dimmable. Some CFL and LED bulbs are specially designed to be dimmed. Check packaging for a "dimmable" icon or notation that indicates the bulb can be dimmed.
You should also look for compatibility information for LEDs as performance may vary by dimmer and the number of lamps connected to any one dimmer.
-

Understanding Color Temperature (CCT)
How cool or warm the light emitted from a light bulb appears to be is known as the correlated color temperature or CCT of the bulb. It’s measured in degrees Kelvin. Most light bulbs fall within a range of 2200K through 6500K. The lower end of the scale (2700K) is where traditional incandescent light sources fall which emit warmer toned light. CFLs and LEDs are available anywhere from warm (2700K) tones to cool daylight tones (5000K).
-

Show Your True Colors Understanding Color Rending Index (CRI)
The light bulb you choose can also affect how you see colors. Ever wonder why your skin looks so bad under old fluorescent lighting? CRI measures how well a light bulb renders colors. Rated on a scale of 0 to 100, with – “0” being poor and “100” being excellent, CRI can help you choose a light bulb that will show colors more accurately. This is more important in areas such as bathrooms where makeup is typically applied or if you have a certain room where projects such as painting, sewing, or drawing might be done.
-

How Bright is Bright? Watts Versus Lumens – How to Choose Brightness
An old way of picking your light bulb is going by the “wattage”. However, with new technologies emerging that use a fraction of the power of traditional incandescents this method isn’t going to work anymore.
You’ll need to start checking for “lumens”. “Lumens” is the measure of how bright a light source is and to pick an alternative with the right amount of light, you’ll need to know how many lumens your replacement requires.
Use the chart below to identify your required lumen rating and then check packaging for bulbs with a similar brightness.
-

-
Did You Know?
Two of the most recognizable and most commonly used bulbs in your home are the incandescent A19 and the halogen reflector or PAR. Although these were both great lighting accomplishments, studies have shown that these are inefficient light sources today.
In 2007, Congress passed a law to encourage the use of more efficient bulbs nationwide. According to this new legislation, the Energy Independence and Security Act (EISA), all light bulbs must be up to 30% more efficient as of January 1, 2012.
Now is the time to select an energy efficient alternative without losing the light you need. Here is a summary of old versus new light bulb technologies. The most important thing to note is that BRIGHTNESS which is measured in “lumens” does not change when choosing a new energy efficient alternative. What does change is the amount of energy consumed. Wattages will differ by manufacturer but here is a general guide of where they might end up. -
It's All About LED
Color Rendering Index for LED Bulbs–
A bulb’s capacity for producing correct-looking colors is measured by its score on the color rendering index. This figure, usually referred to as the CRI number, is a score out of 100. The CRI is comparing the lights to the colors reproduced by daylight.
A high CRI number is like a high grade point average for color quality. While most LEDs score in the 80s (a solid B average), quality continues to improve & CRI rating increases. Lower price LED’s may have a lower CRI rating.
Color Rendering Index is the ability of a light source to reproduce the colors of the object it is illuminating faithfully in comparison with a natural light source. The CRI is an index from 1 to 100, 100 being a perfect score (e.g. sun light). Those ugly yellow parking lot lights (high pressure sodium lights) have a CRI of 49. The reason we are not a fan of fluorescent lighting is because most of them are in the 60’s and 70’s range and do a poor job of accurately reproducing color. This is especially true in a home where great care is taken in selecting fabrics for furniture, paint color for walls, and floor coverings.
Look for high quality LED lighting to ensure the consistency of the color temperature across multiple products. If you retrofit your kitchen with 10 LED can lights, it is important that all 10 produce the same “white” light.
-

LED Features-
- LEDs are not always compatible with traditional dimming switches.
- You may choose to replace the dimmer or shop for a LED bulb that states it is dimmable.
- If you’d like your LED to be dimmable, you need to do one of two things: find LED bulbs compatible with traditional dimmers, or replace your current dimming switch with a leading-edge (LED-compatible) dimmer.
- When shopping for LEDs, it helps to know what kind of dimming switch you have, but if you don’t know (or would rather not go through the trouble), simply search for LED bulbs compatible with standard incandescent dimmers.
- Plan for where the bulb will be used (so you get the full expected life span from the bulb)
- LED’s run considerably cooler than incandescent bulbs, but the still do produce some heat. The heat is pulled into the heat sink at the base of the bulb to be dissipated.
- Keeping LED bulbs cool helps keep the promise of a very long live.
- Consider where you’d like to place your LED fixtures. If you have fully or semi-enclosed fixtures you need to light up, look for LEDs that are approved for recessed or enclosed spaces.
-
In Closing You don’t have to make a huge commitment now. If you want, you can upgrade to more efficient lighting one room at a time, or as old light bulbs burn out. Start with the fixtures that get used the most for maximum savings. Or start with installing an LED light bulb in a hard-to-reach spot, like a cathedral ceiling fixture, since you won’t have to replace it for many, many years.
Think to yourself- I will save money long term. I am helping the environment and I have less chances of falling off a ladder & hurting myself.
The sooner you make the switch, the sooner you’ll start saving.
-
Recently Viewed












